Habilmind >
Related to Students' Academic Performance > General Learning Skills
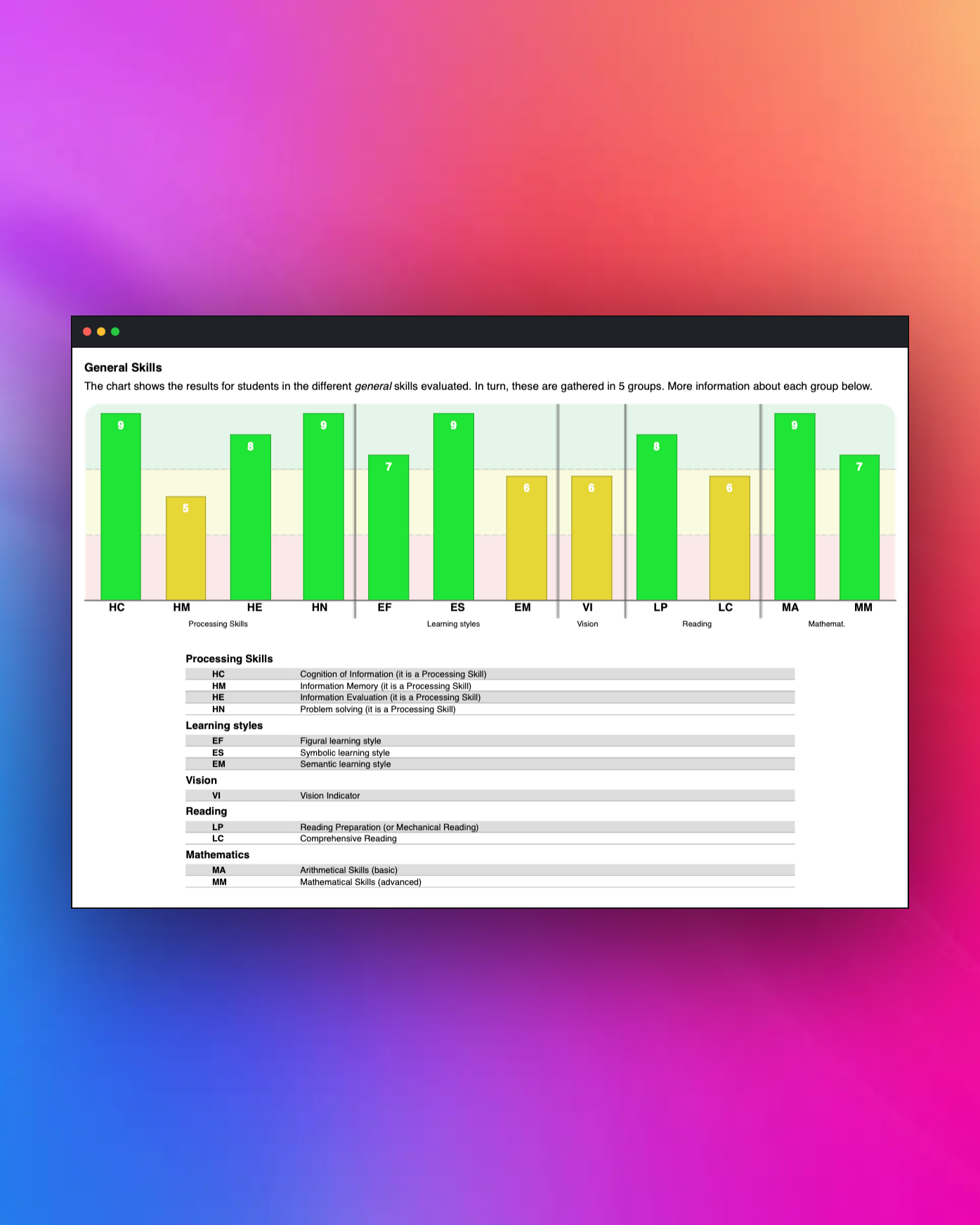
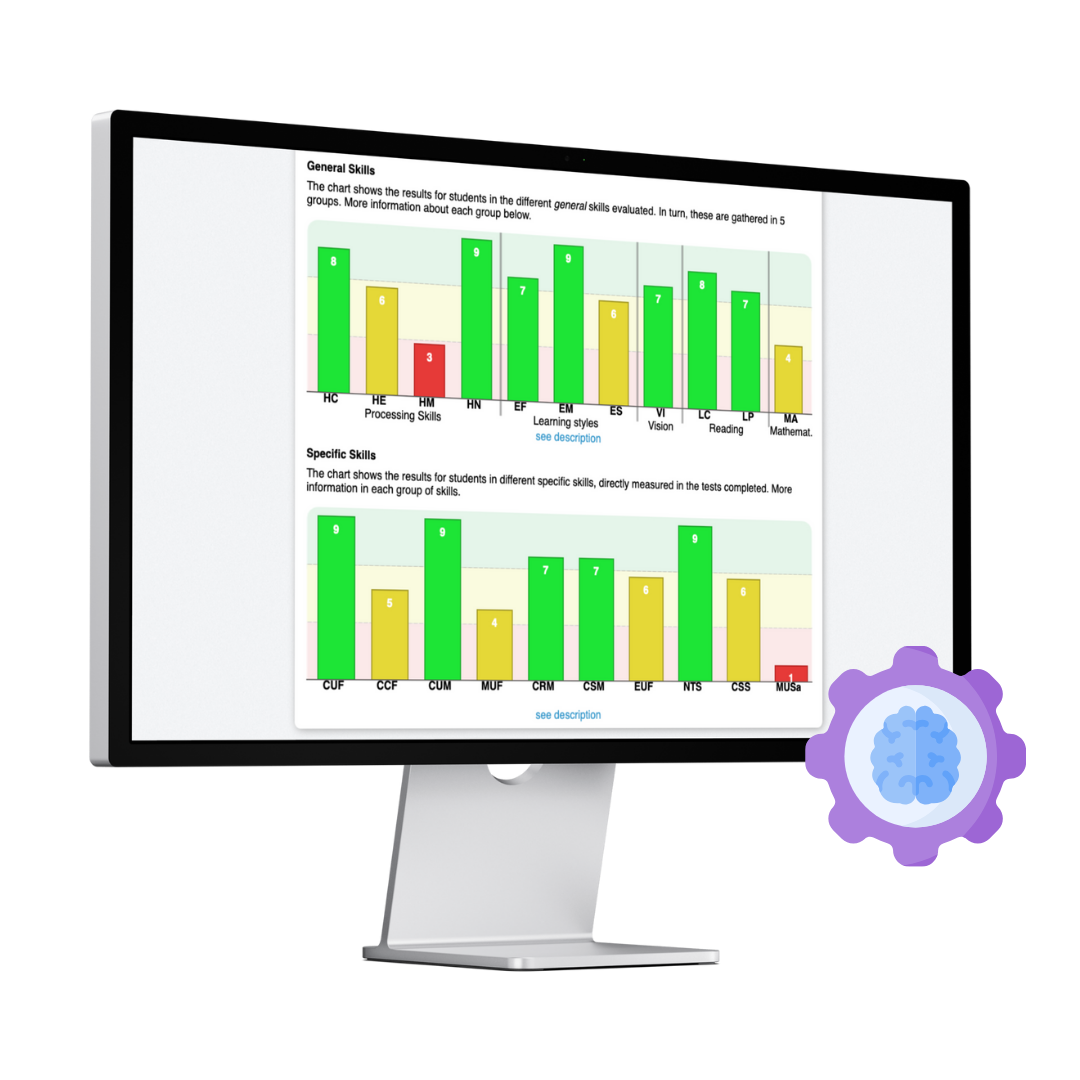
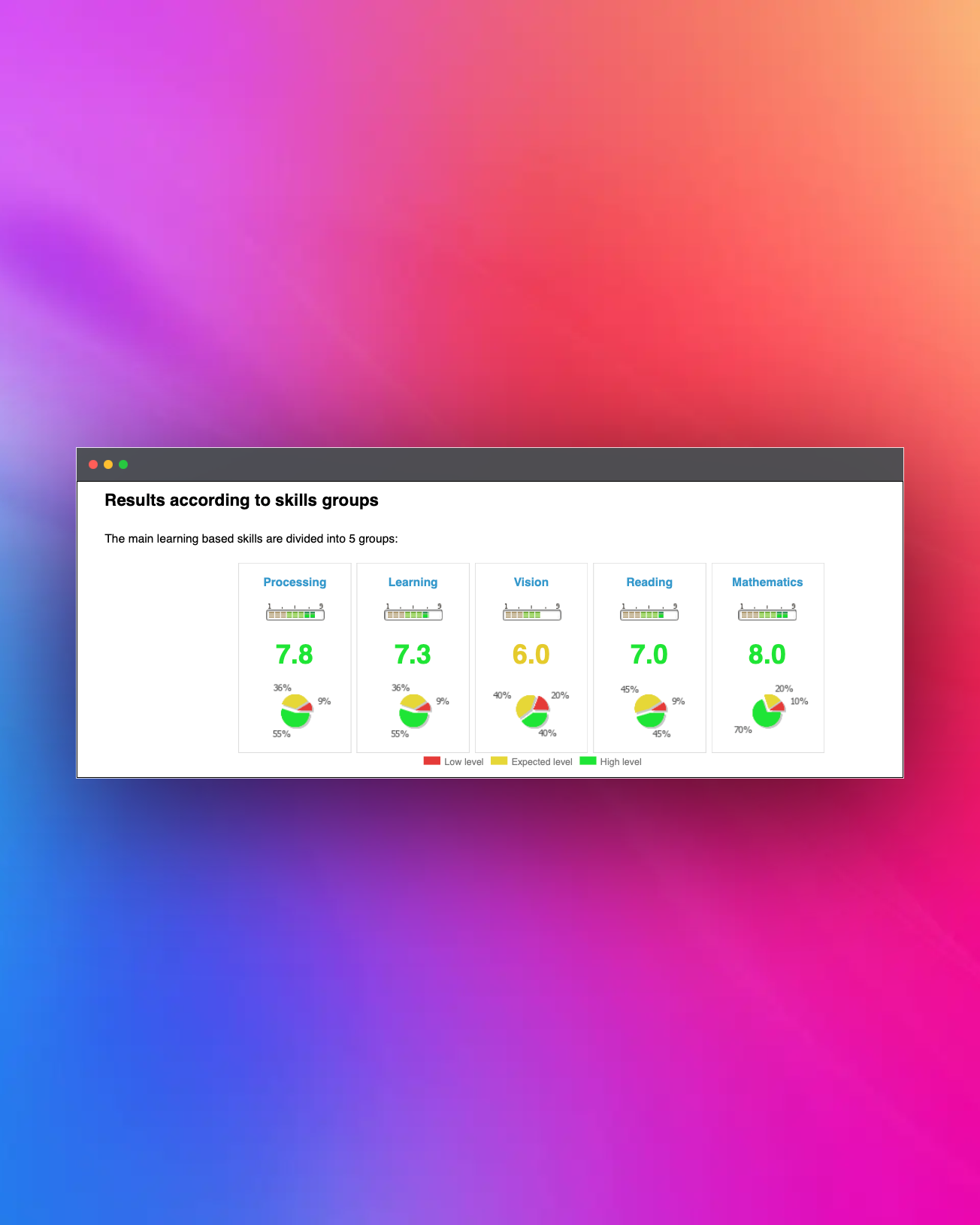
General Learning Skills
Analysis of the 22 cognitive skills
Assessment through a criterion-referenced test to measure the development level of cognitive skills essential for learning and professional performance.
ℹ️Application: Collective and individual
🕓Duration: 2 to 3 sessions of 45 minutes each
✅ Applicable age: 6 years and above
Authors

Isauro Blanco
Researcher and speaker specialising in cognitive development.

Habilmind R&D&I Team
Habilmind team dedicated to educational innovation.
What does your school obtain from this tool?
01
Understand
The reasons behind certain learning difficulties.
02
Analyse
High-impact indicators separately.
03
Intervene
Proactively.
04
Recognise and Address
Group diversity.
05
Provide
Accurate information.
Problems you prevent (or mitigate) when using General Learning Skills
1.School failure: Early detection facilitates intervention to prevent learning difficulties from becoming chronic and ensures an appropriate educational response.
2.Difficulties in reading mastery and comprehension: Reading is the foundation of all learning; struggles in this area can impact performance in any subject, including mathematics. This tool helps identify which skills are underdeveloped, allowing targeted stimulation to prevent negative effects on reading competence.
3.Difficulties in learning mathematics: Mathematics is often met with resistance because the root of the difficulty is not identified, leading to reinforcement without addressing the underlying issue. Identifying the source of the difficulty prevents it from becoming a long-term obstacle.
4.Lack of motivation and low academic self-concept: A false belief of low ability due to poor or insufficient school performance directly affects intellectual self-esteem and, consequently, motivation. Understanding their skills, how they influence performance, and how to develop them fosters students' sense of control over their learning and enhances their motivation for improvement.
On which platforms of the Habilmind Ecosystem is this tool available?
Description of the Learning Skills Test by Isauro Blanco
Video in which Isauro Blanco explains the cognitive test Learning Skills
Video tutorial for the General Learning Skills test
Key aspects you should know about the General Learning Skills test. Explanation and tour of the platform.
Try it for free, with no obligation
Request access to the tool through the "FREE REGISTRATION" button to explore it first-hand.
(*) Free trials are available for schools, colleges, institutes, universities, clinical psychologists, and researchers.